Among the different types of electromagnetic waves, radio signals are used very widely in our lives. Cue in this widespread usage, they have a major effect on RF antennas themselves and RF antenna design.
RF, visible, ultra-violet and infrared all comprise electromagnetic waves differing from each other in wavelength and frequency. These are made of both electric and magnetic components, which are inseparable. Forming a 3D structure, the individual fields are at right angles to one another and to the direction of motion of the wave at the same time.
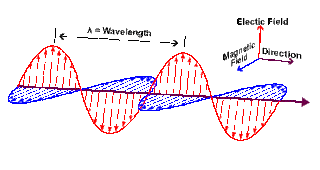 |
| EM wave field directions |
In antennas,Basic electric fields generally result from voltage changes in RF radiated signal whereas the magnetic changes cue into the current flow. The electric field lines often run along the same axis as the RF antenna, spreading out as they move away. It is measured in terms of the change in potential, over a given distance, e.g. volts per meter, and is hence called field strength. Similarly on reception of a signal the magnetic changes would cause a current flow, resulting in an electric field, which in turn causes voltage changes on the antenna.
Among the major concepts/properties of a wave, the first is its wavelength, measured as the distance between two similarly identical points. To resolve any confusion the previous line might have made, we can measure the wavelength from one peak to the peak, or one trough to the next. A peak is the highest or the positive maximum value, whereas a trough is the lowest or the negative highest value of the signal. Since these are easy to identify in a wave, the wavelength can be very easily calculated.
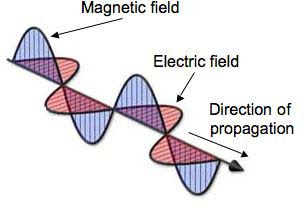 |
| EM wavelength |
RF travel at the speed of light. For calculation purposes, it is considered at 300 million meters per second, whereas the exact value would be a little less.
Frequency-Wavelength Correlation Relating wavelength frequency and energy
FREQUENCY-WAVELENGTH CORRELATION:
Frequency is often used as a measure of the signal. Frequency and wavelength are relate to each other by the below relation:
λ = c / f
where
- λ is the wavelength, in meters
- f is frequency, in Hertz
- c is the speed of light, in meter / second
- Field measurements
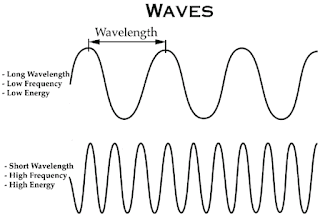 |
| Relating wavelength frequency and energy |
Similar to a transformer, there is also an inductive field close to the RF antenna. This can often cause distortions in the original measurements in the nearby signals since this is not the intended signal. This often becomes a hassle with multiple antenna transmitting at close proximity. This causes interference at the receiving end of the antenna as well. Additionally, the wiring for electricity and other transfer might also cause signal distortions. The saving grace here would be the fact that, it starts to fade away after a couple of meters.
Theoretically speaking, the waves should be accepted by the antenna and we should have an output. However reality is not so simple. The waves are affected by polarization, resulting in some miscommunication of signal. RF antennas and the EM waves both undergo polarization.
For an electromagnetic wave, polarization is effectively the plane in which the electric wave vibrates. This is important when looking at antennas because they are sensitive to polarization, and generally only receive or transmit a signal with a particular polarization. In an antenna, polarization is in the same plane as the elements of the antenna. It is easy to determine since a horizontal antenna receives horizontally polarized signals and similarly for vertical antenna.
Matching the polarization becomes an important factor to have the best reception of signals. If the antenna polarization does not matches with that of the signal, there is a decrease in the level of signal by a factor of cosine of the angle between the polarization of the antenna and signal. If the two are cross polarization with one another, then theoretically signal reception should not be possible.
Theoretically speaking, the waves should be accepted by the antenna and we should have an output. However reality is not so simple. The waves are affected by polarization, resulting in some miscommunication of signal. RF antennas and the EM waves both undergo polarization.
For an electromagnetic wave, polarization is effectively the plane in which the electric wave vibrates. This is important when looking at antennas because they are sensitive to polarization, and generally only receive or transmit a signal with a particular polarization. In an antenna, polarization is in the same plane as the elements of the antenna. It is easy to determine since a horizontal antenna receives horizontally polarized signals and similarly for vertical antenna.
Matching the polarization becomes an important factor to have the best reception of signals. If the antenna polarization does not matches with that of the signal, there is a decrease in the level of signal by a factor of cosine of the angle between the polarization of the antenna and signal. If the two are cross polarization with one another, then theoretically signal reception should not be possible.
WHAT IS POLARIZATION?
Since it is making such a big issue with EM waves, let’s look at it in simple terms. In simple terms, the ability of waves to oscillate in more than one direction can be termed as polarization. In an EM wave, both the electric and magnetic fields oscillate in different directions. Conventionally, the polarization of light refers to the changes of electric field. Depending on the direction of the oscillations, we have certain categorizations.
Polarization is an important parameter in areas of science dealing with transverse wave propagation, such as optics, seismology, radio, and microwaves. Especially impacted are technologies such as lasers, wireless and optical fiber telecommunications, and radar.
CLASSIFICATION:
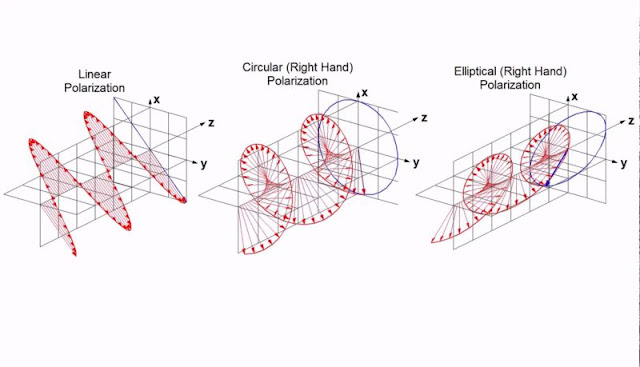
To define and understand it properly, we have certain categories that a wave undergoes. A broad classification would be linear and circular. Linear polarization can be further subdivided into two categories, vertical and horizontal.
These are the simplest forms and are easy to understand. For eg. to generate a horizontal polarized wave, we could have an antenna axis horizontal to the earth. The electric field vector of the EM wave will be parallel to the earth. Similarly for a vector polarized EM wave, we could have an antenna vertical to the ground. The electric field vector is now perpendicular to the ground.
Circular polarization however is a little complex. A comparison for understanding, could be a signal propagating from a rotating antenna. The signal would appear to be helical, as seen from the axis. This can again go either way. As seen from the transmitting antenna, left winding spiral, is a left circular polarized, whereas a right winding spiral is a right circular polarized wave.
Another form is elliptical polarization. This would be more close to the real life situations of the signals. It occurs due to a mix of linear and circular polarized waves. A visualization for the wave would be the tip of the electric field vector tracing an elliptical path in propagation.
RECEPTION AT ANTENNA:
At the reception end, the story is however not as ideal as theory. Since polarization requires setting up of antenna at the transmission end, same is true at the reception end. But unlike a linearly polarized antenna transmitting linearly polarized waves, a receiver can receive other polarized signals as well. Looks like a receiver is the AB+ of signals.
The factor to note however here is that, the signals received would be below 3 dB levels. Which would mean the signal would be very weak, and hence would not the best option to go for while designing a system. Similar is true for any signal reception. The signal reception is optimum for polarization match of wave and antenna.

Post a Comment